After the 20th century, the garment industry gradually became a large-scale manufacturing industry. Moving from manual production (Costments are sewn according to the number of measurements per person at a rather expensive cost) to industrial production, serving the needs of the masses at a low cost. New clothing models are constantly born with styles, patterns, quality, diverse colors, and prices suitable for many different customer segments. The production stage continuously moves to a place with low production costs, from North America, Western Europe to Spain, then to Hong Kong, Taiwan, Korea, to China and transfer oil to South Asian countries and Latin America.
For Vietnam, the industry is the industry with the second largest export turnover in the country, which has made a large number of workers (more than 20% of the workers in the public sector and nearly 5% of the total labor force in the country). However, export turnover is mainly from FDI enterprises. FDI enterprises in the field of garment production, although only accounting for about 25% of the quantity, contribute to more than 60% of export turnover.

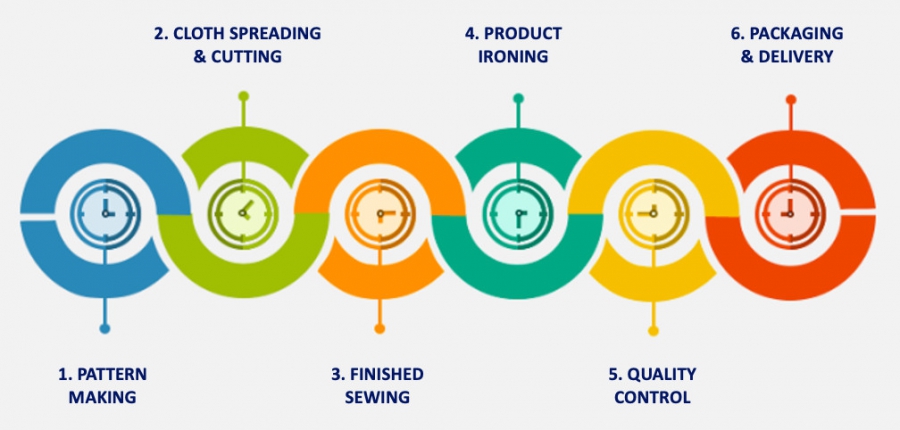
PRODUCTION PROCESS
In 2020, the total export turnover of textile and garment products reached about 35 billion USD, down 9.8% compared to 2019. In 2021, although Vietnam's socio-economic situation was greatly affected by the epidemic, most businesses in the industry had orders until the end of the third quarter and even by the end of the year. The reason for this recovery is that the demand for consumer goods in the main export markets of the US, the European Union (EU), Japan, etc. has increased significantly. Currently, textile and garment businesses have stable orders. Therefore, the target of reaching 40 billion USD of export turnover of the textile and garment industry in 2021 is completely positive.
However, in the way ahead, the textile industry is facing many challenges from the complex development of the epidemic. According to the Vietnam Textile and Garment Association, at least 45 textile and garment enterprises have had to suspend production since the Covid-19 outbreak again in May 2021. Factories are forced to stop operating under pressure to both "pay" production costs, and worry about the source of money to pay wages for workers, and then fear of compensating customers or having to change more expensive shipping methods to meet delivery time. Just 14-21 days of production suspension will directly affect the production plan for the whole year 2021.

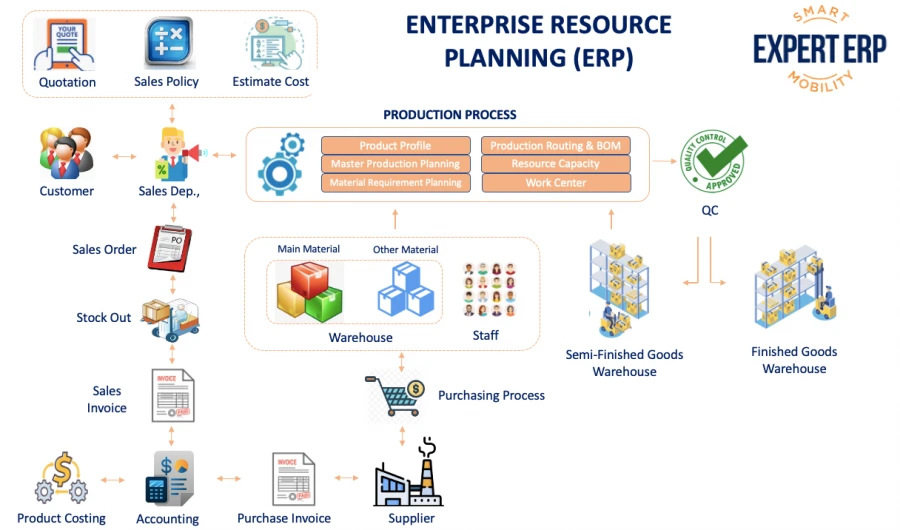
Textile and garment enterprises produce or process mainly according to Orders/Contracts, so the monitoring process from the Business stage - Production planning - Preparation of production materials - Production statistics - Warehouse semi-finished products - finished products must be attached to Orders/Cons contracts.
For Sales Department:

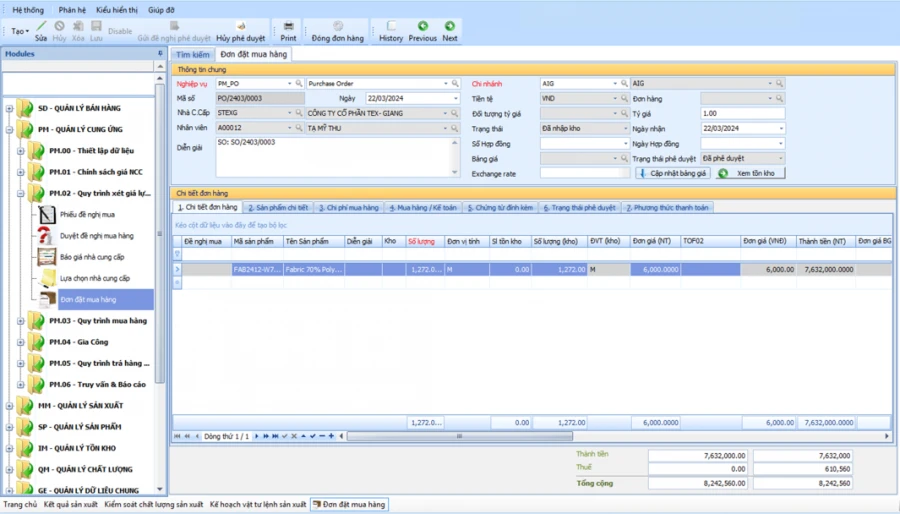
For the Purchasing Department:

For Warehouse Management:

For Production Management:

For Machine and Equipment Management:



Allow to manage multiple revisions:
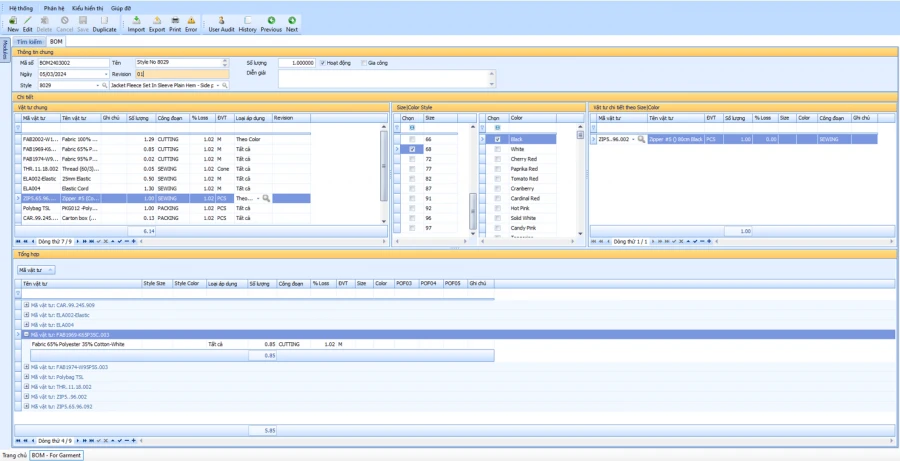
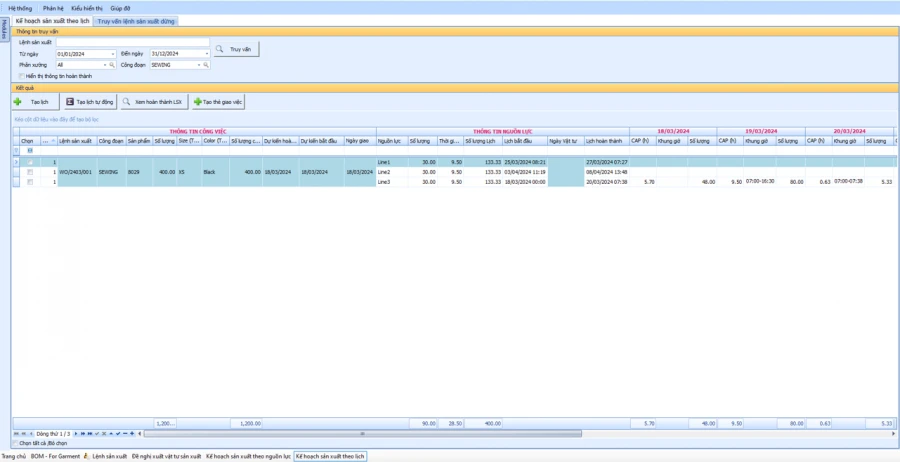
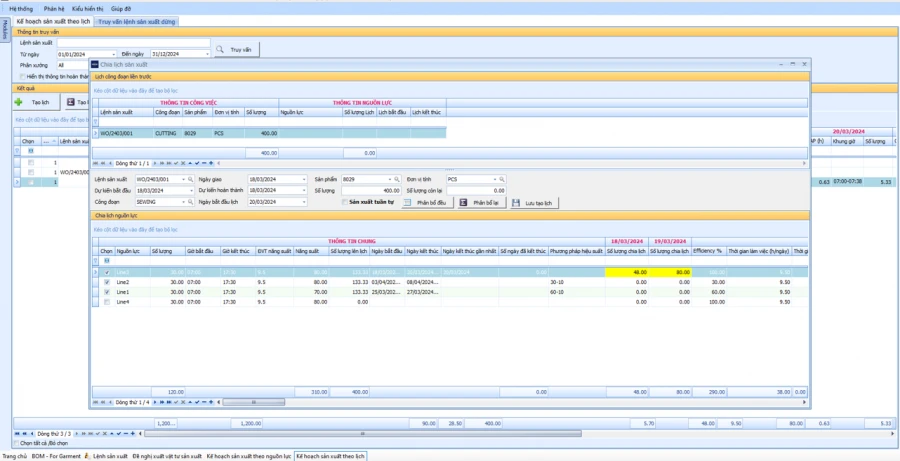
The system automatically calculates the details of the work to be produced for each BTP detail, stage. Is the basis for the plan to issue assignment cards to each workshop/transmission
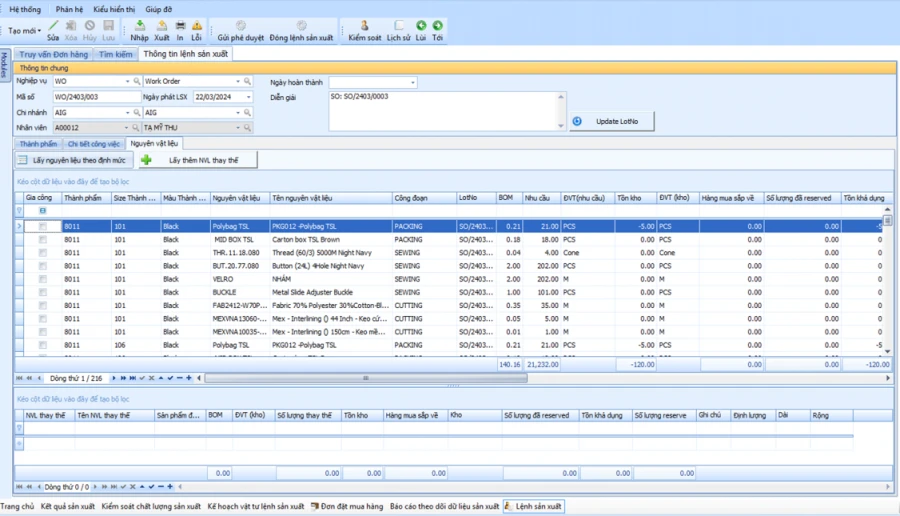
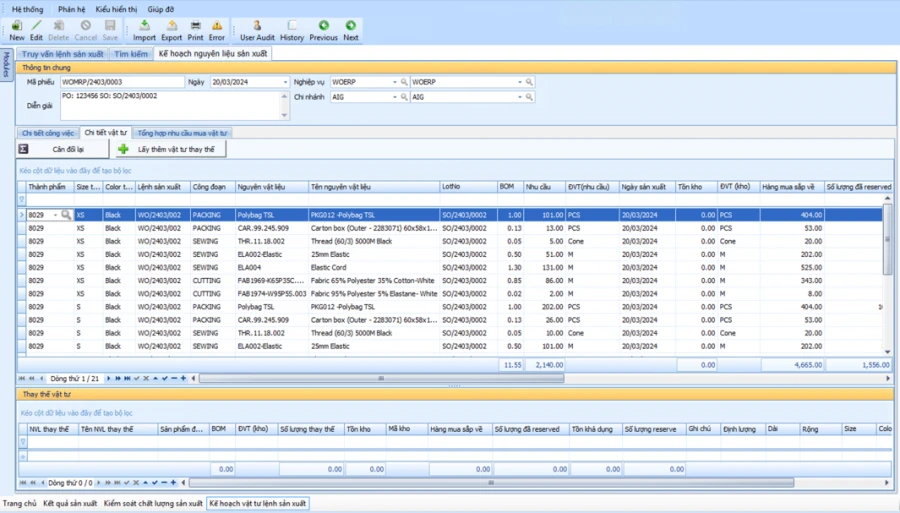
The system allows the balance of processed goods: Based on the processing balance, recalculate the details of the work to be produced and offer purchase/expossion
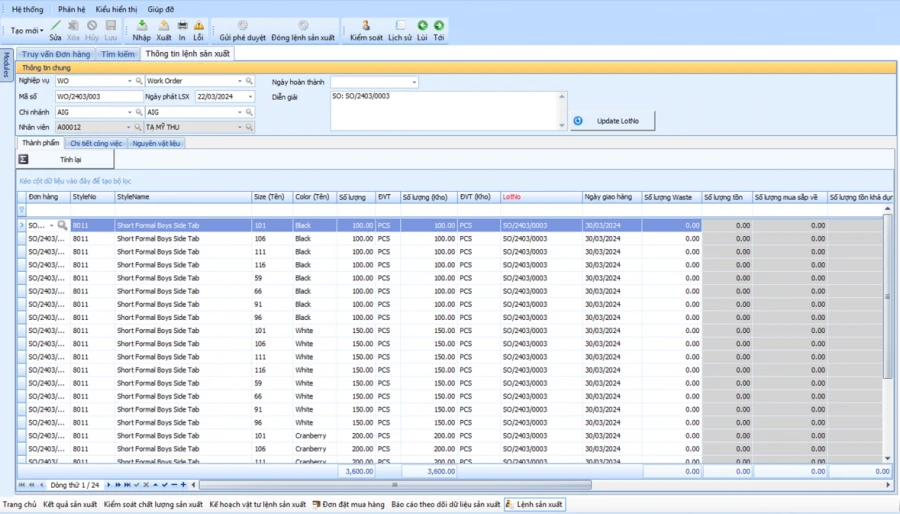
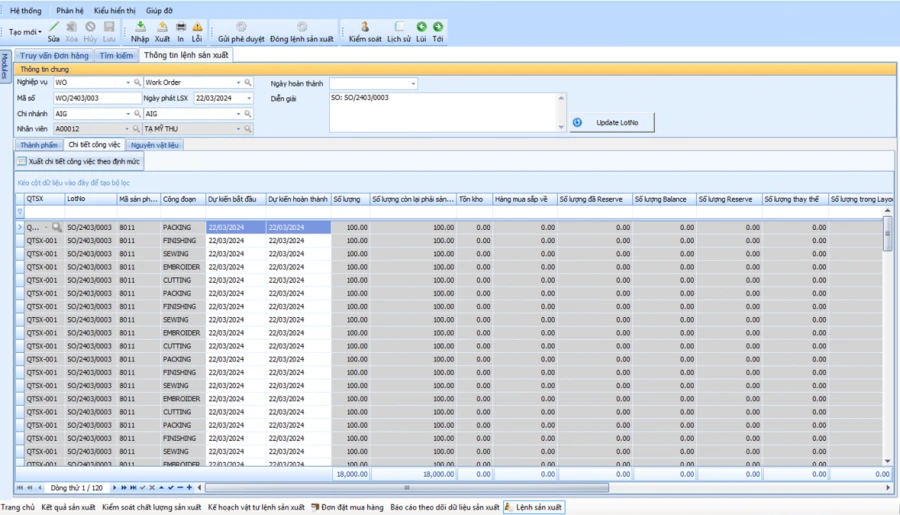
Automatic calculation system:
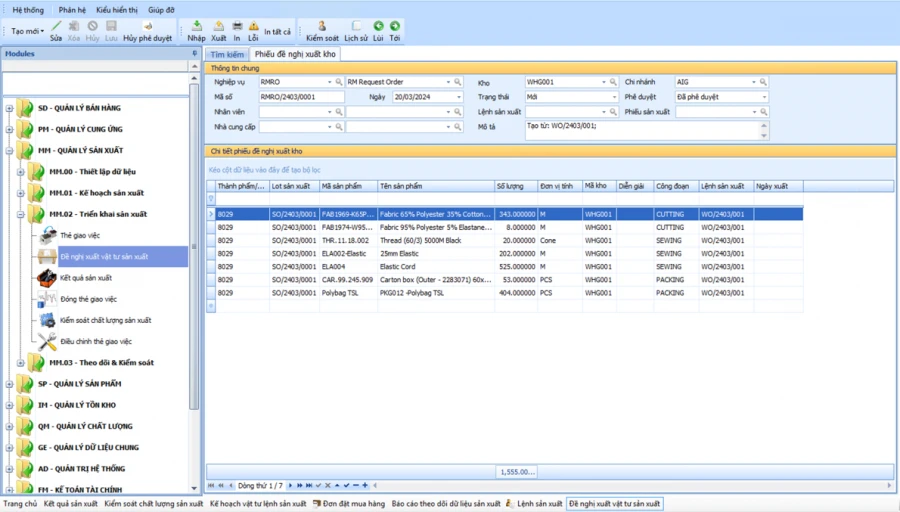
The software allows:
Ability:
Ability:
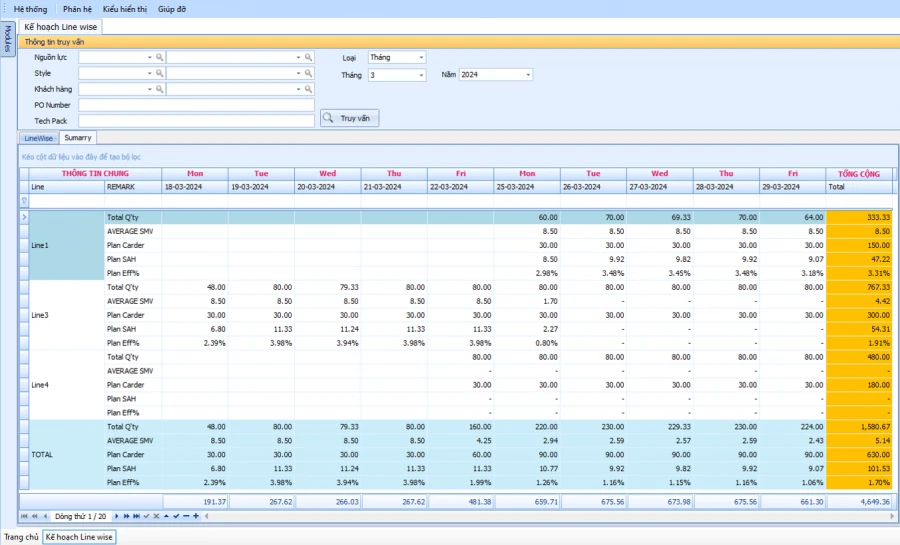
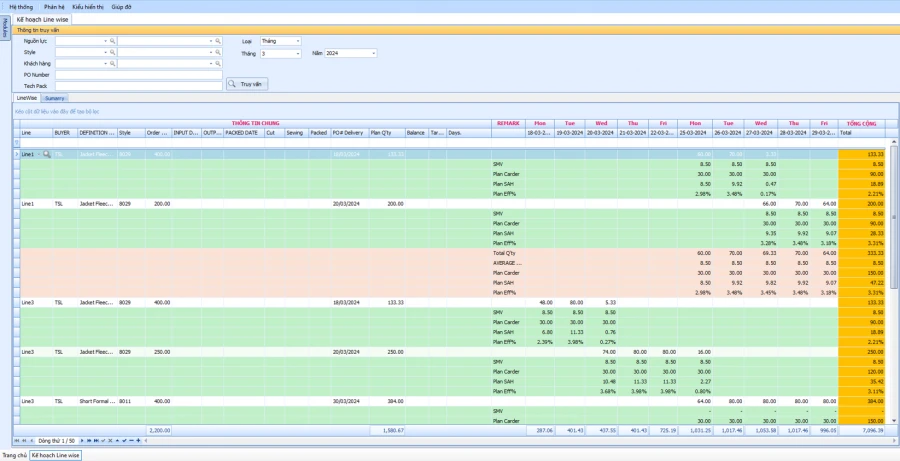
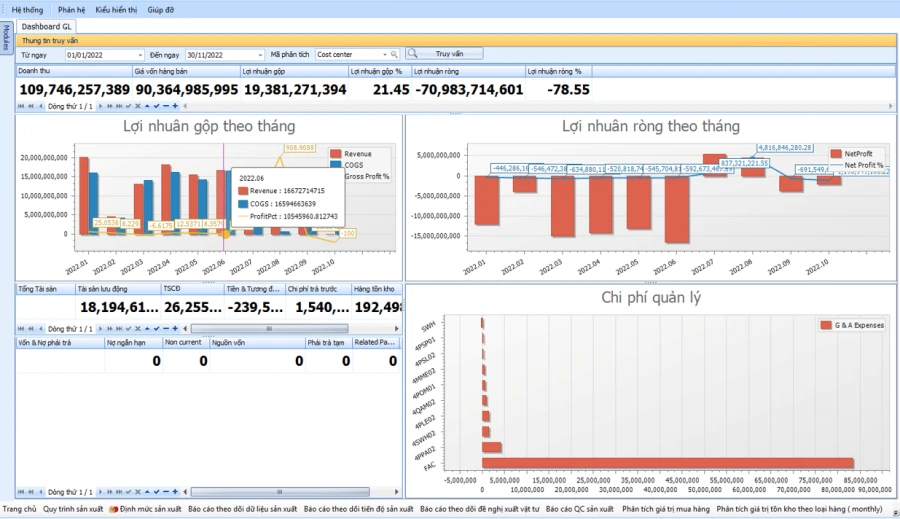
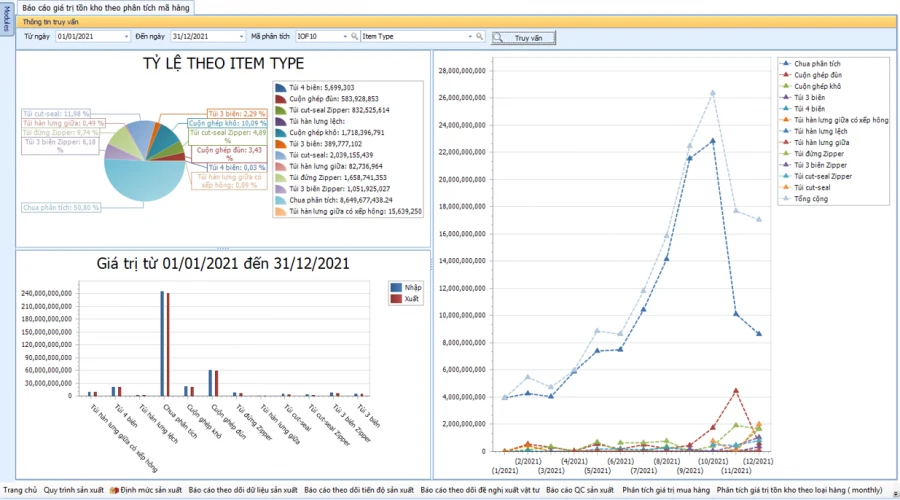
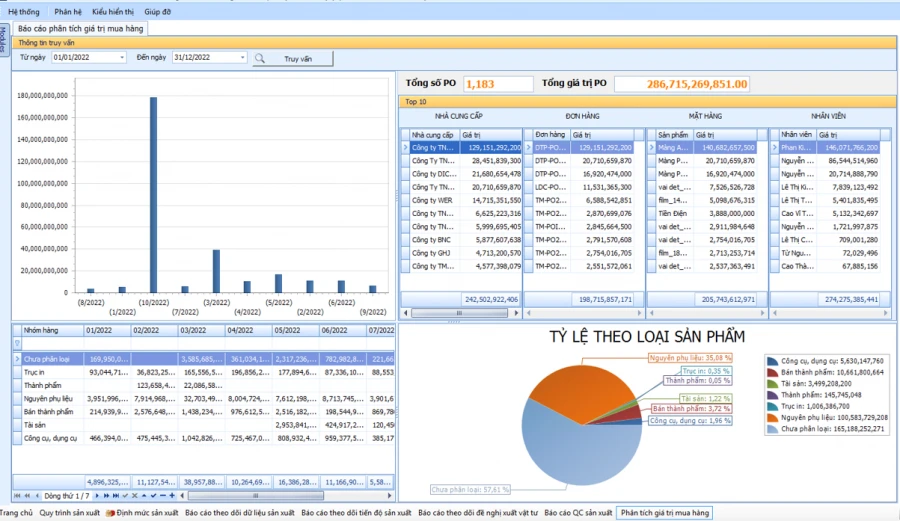
SMART REPORT
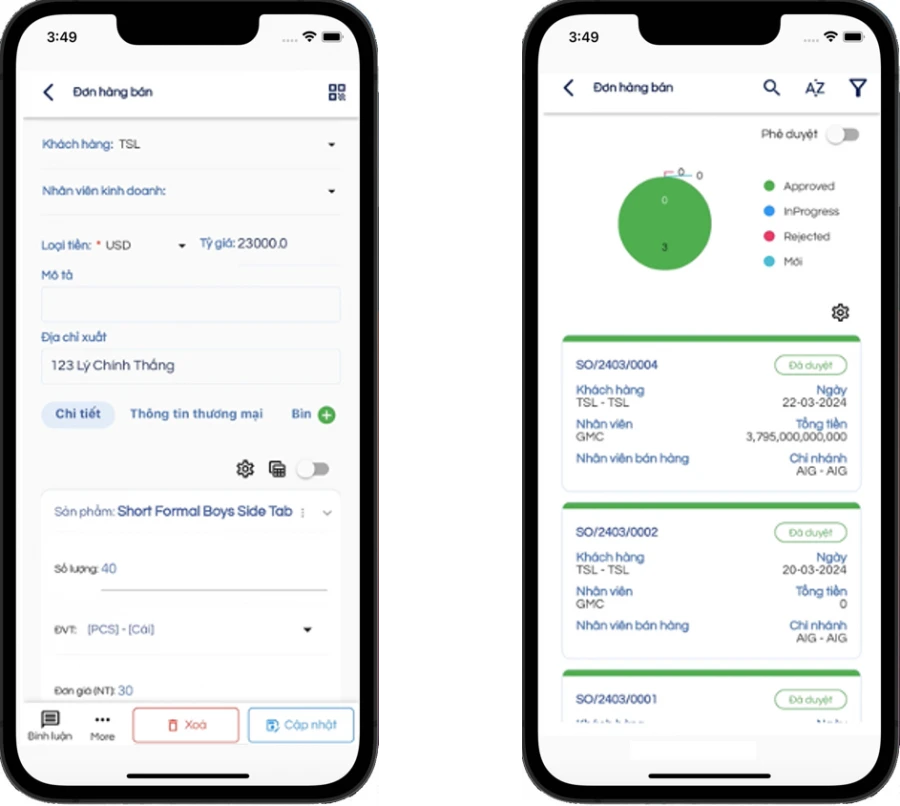
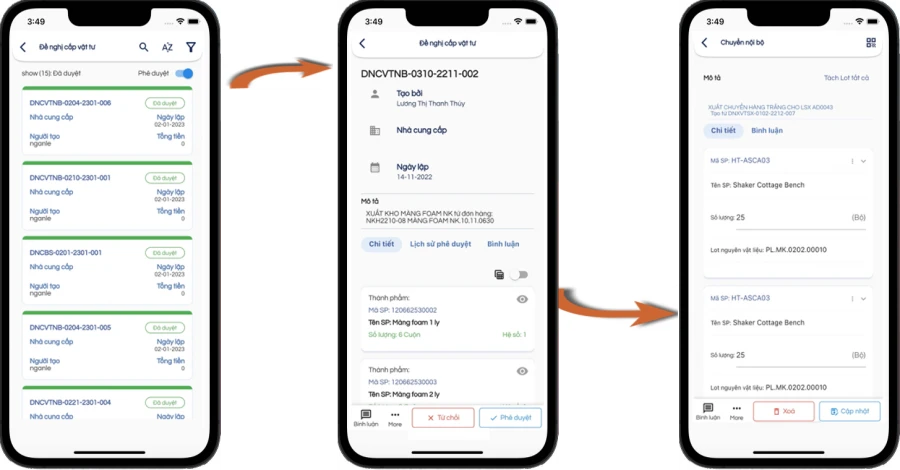
ORDER REVIEW
CONTROL THE LEVEL OF PRODUCTION MATERIALS
PRODUCTION SCHEDULE ACCORDING TO PRODUCTION BATCH AND LINE
(TEXTILE INDUSTRY)
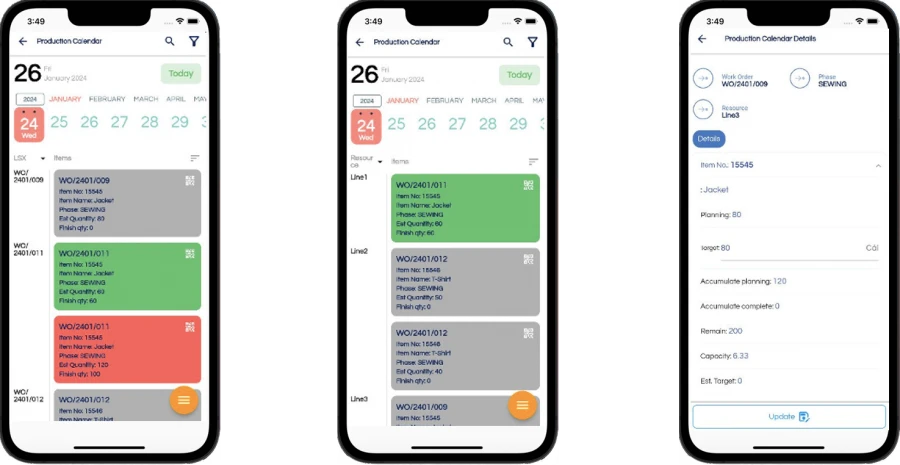
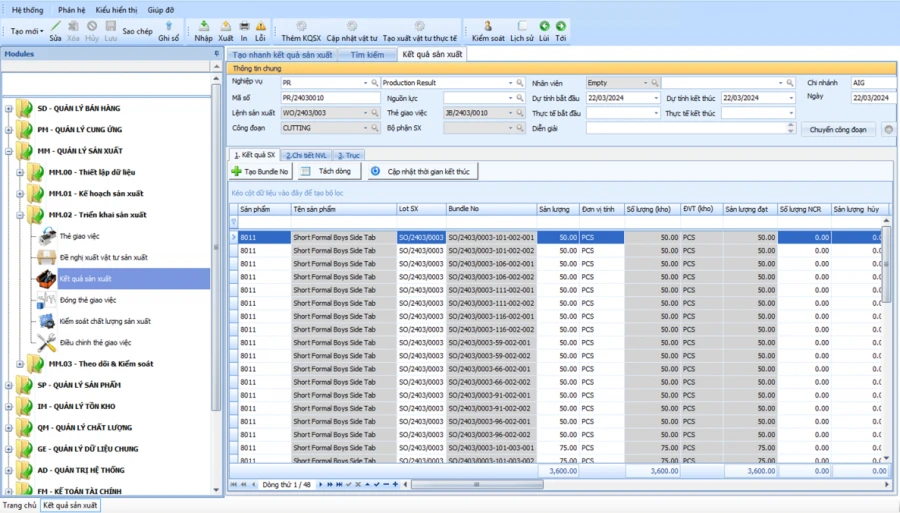
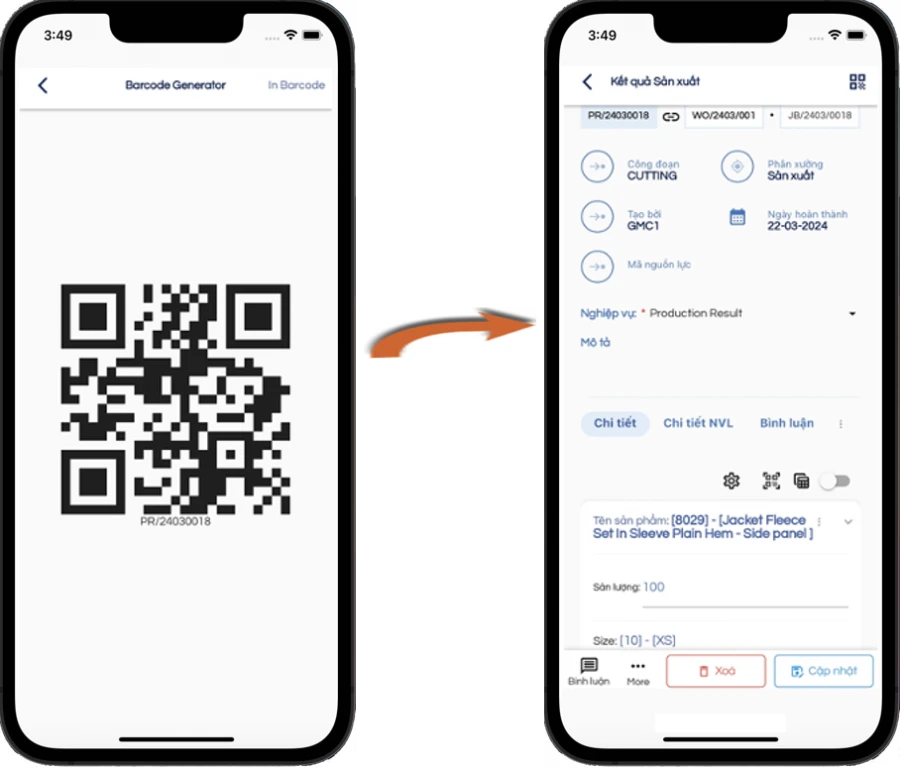
RECORD PRODUCTION RESULTS
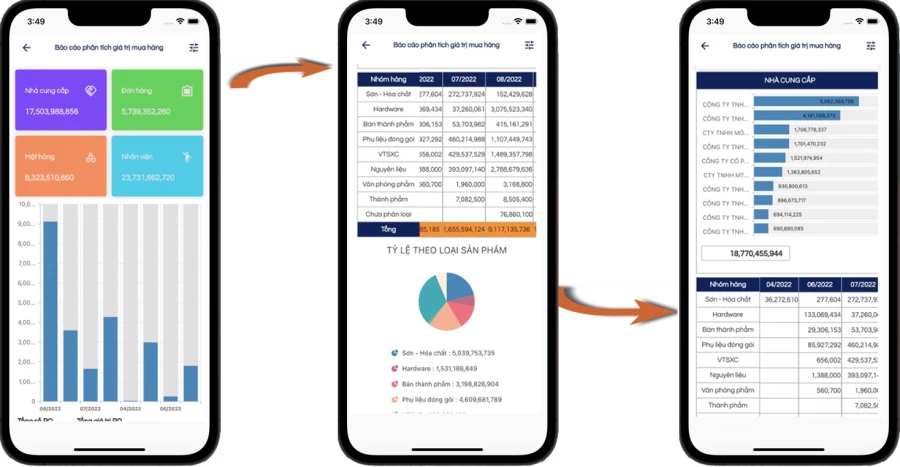
ANALYSIS OF PURCHASE SITUATION
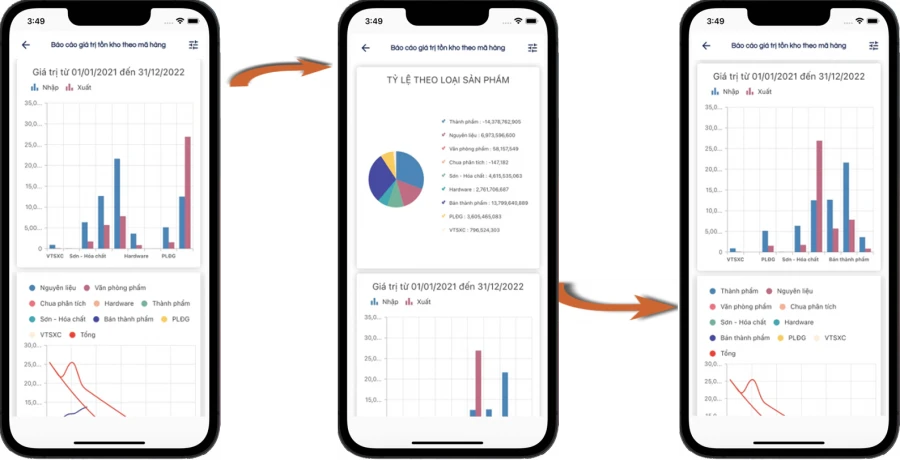
INVENTORY VALUE ANALYSIS
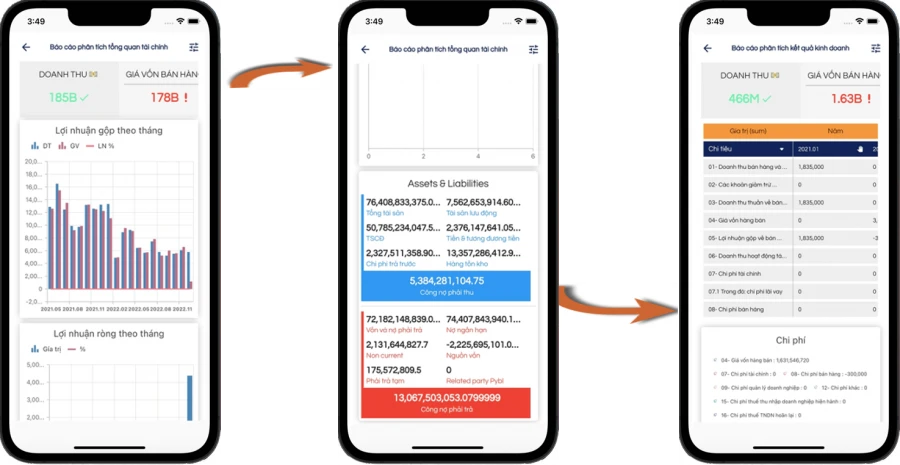
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL SITUATION